The field of accounting is built upon a set of fundamental principles that serve as the bedrock for financial reporting and analysis. These fundamental accounting principles provide a framework for businesses to record, summarize, and communicate their financial information accurately and consistently. By adhering to these principles, organizations can ensure the reliability and comparability of their financial statements, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions.
Table of Contents
Accrual Basis Accounting: A Key Principle for Recognizing Transactions
One of the fundamental accounting principles is accrual basis accounting. Unlike cash basis accounting, which records transactions only when cash is received or paid, accrual-basis accounting recognizes transactions when they occur, regardless of the associated cash flows. This principle ensures that revenues and expenses are recorded in the period in which they are earned or incurred, providing a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position and performance.
Going Concern Assumption: Preserving Continuity in Financial Reporting
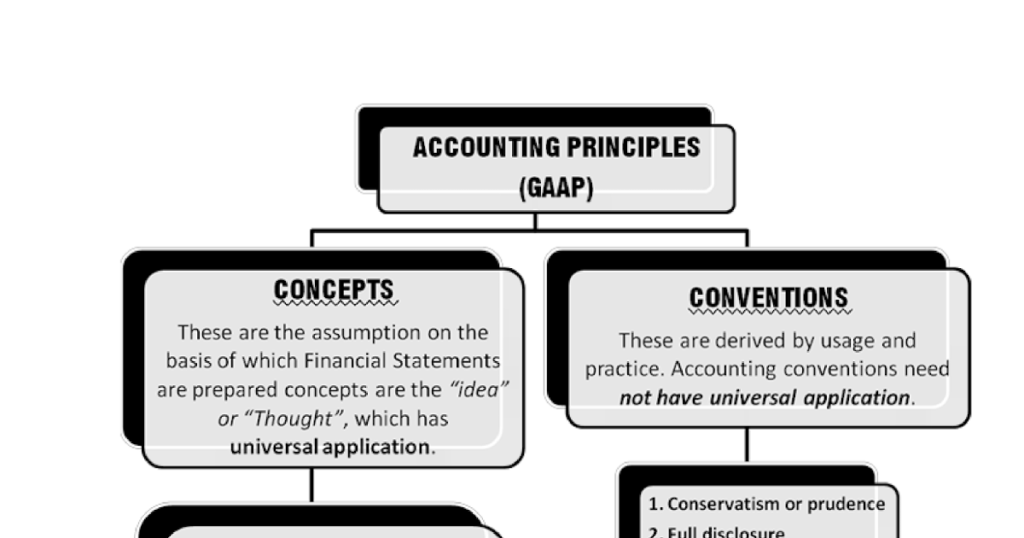
The going concern assumption is another essential fundamental accounting principle in accounting. It assumes that a business will continue its operations for the foreseeable future, allowing financial statements to reflect this continuity. This principle is crucial in valuing assets, and liabilities, and determining the appropriate timing of revenue recognition. By assuming the business will continue, stakeholders gain a better understanding of the company’s financial health and prospects.
The Principle of Consistency: Ensuring Uniformity in Financial Reporting
Consistency is a fundamental accounting principles that requires businesses to use the same accounting methods and principles from one period to another. By maintaining consistency in financial reporting, companies provide comparability and allow stakeholders to analyze trends over time. This principle also ensures that changes in accounting policies are adequately disclosed and justified, minimizing confusion and promoting transparency.
Materiality: Focusing on Significant Information
Materiality is a principle that emphasizes the importance of reporting information that could influence the decisions of financial statement users. This principle recognizes that not all information is equally significant and encourages businesses to focus on reporting material items that could impact the evaluation of their financial performance and position. Materiality is subjective and requires professional judgment in determining what information should be included in financial statements.
Historical Cost: The Basis for Valuing Assets and Liabilities
The principle of historical cost states that assets and liabilities should be recorded at their original acquisition cost. This principle provides a reliable basis for financial reporting, as it avoids potential biases and subjective valuations. While the historical cost principle may not reflect the current market value of assets and liabilities, it ensures consistency and comparability across different periods.
Full Disclosure: Transparency and Communication
Full disclosure is a principle that promotes transparency in financial reporting. It requires businesses to provide all relevant information necessary for stakeholders to make informed decisions. This includes disclosing significant accounting policies, contingencies, related party transactions, and any other material information that could affect the interpretation of financial statements. Full disclosure enhances the credibility and reliability of financial reporting.
Matching Principle: Aligning Expenses with Revenues
The matching principle is a fundamental accounting principles that guides the recognition of expenses in financial statements. It states that expenses should be recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate. By aligning expenses with the revenues they contribute to, the matching principle ensures that financial statements accurately represent the costs incurred in generating revenue, allowing for a more accurate determination of profitability.
Objectivity: Impartial and Reliable Financial Reporting
Objectivity is a fundamental accounting principles that requires accountants to present financial information without bias or personal judgment. It emphasizes the importance of using verifiable and reliable evidence when recording and reporting financial transactions. By adhering to the principle of objectivity, financial statements gain credibility and can be relied upon by stakeholders to make sound decisions.
Understand the Fundamentals for Sound Financial Management

By exploring and understanding the fundamental accounting principles, businesses can establish a strong foundation for sound financial management. These principles provide a framework for accurate and reliable financial reporting, ensuring transparency, comparability, and informed decision-making. Implementing these principles helps businesses maintain credibility, gain investor confidence, and navigate the complex landscape of accounting regulations and standards.
Conclusion-Fundamental Accounting Principles
The fundamental accounting principles discussed above play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and transparency of financial reporting. From accrual basis accounting to full disclosure, each principle contributes to the overall integrity of financial statements. By adhering to these principles, businesses can provide stakeholders with a clear and comprehensive view of their financial position and performance, enabling better decision-making and fostering trust in the financial markets. Understanding and implementing these fundamental accounting principles is crucial for any organization aiming to achieve sound financial management and long-term success.
Learn about : Secure your business’s financial interests with the expertise of top finance law firms in the UK, ensuring legal compliance and strategic guidance for lasting success.






